Clear reduction in CO2 emissions in European cities as a result of COVID-19 lockdown
Reduction in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in seven European cities during the COVID-19 lockdown was shown in a recent study published on the official website of ICOS (International Integrated CO2 Monitoring System). Although this reduction is not large enough to be detectable on a planetary scale in the atmosphere, significant changes in CO2 emissions can be observed locally. They can also be directly measured at near real-time with micrometeorological tools such as the eddy covariance (EC) technique. EC is used globally to study ecosystem-atmosphere exchange of CO2, and the number of urban flux measurement towers has been growing steadily over the past couple of decades.
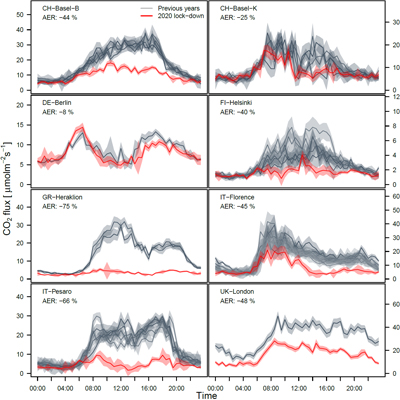
The European cities included in the study are: Heraklion in Greece, Basel in Switzerland, Berlin in Germany, Florence and Pesaro in Italy, Helsinki in Finland, and London in the UK, in which, flux towers have been installed with appropriate equipment for direct measurement of CO2 flow from the 3D urban surface into the atmosphere. Reductions in emissions ranged from 8% in an urban area of Berlin with a significant percentage of vegetation, to more than 70% in the center of Heraklion. Real time observations from the Heraklion flux tower that is operated by FORTH are available at: http://rslab.gr/heraklion_eddy.html
Dr. Nektarios Chrysoulakis, head of the Laboratory of Remote Sensing Research and Applications in Urban and Natural Environment (http://rslab.gr ) of the Institute of Computational Mathematics of FORTH, and Dr. Stavros Stagakis, postdoctoral researcher, participated in the international research team conducting this study.
"The reduction in CO2 emissions varies in the different urban areas examined, due to the different local characteristics and the different level of severity of the restrictive measures in each country. However, in all cities, a clear correlation was found between emission reductions and traffic restrictions. The largest reduction of emissions was observed in Heraklion, as the flux tower of FORTH is located in an area characterized by dense commercial activity and intense traffic, factors that completely stopped during the quarantine", Dr. Nektarios Chrysoulakis explained.
The publication on the ICOS website is accessible at https://www.icos-cp.eu/event/933
Detailed description in pdf file at the link:
https://data.icos-cp.eu/objects/w6pTmRGYKqAm3c-siQrg5kgd
For more information, you can contact Dr. Nektarios Chrysoulakis (tel .: 00302810391762, email: zedd2@iacm.forth.gr